Construction classifies a building’s foundation under the sub-structure stage because it lies below the natural ground level. It’s the most critical stage in the building construction since it distributes the weight of the building to the ground. The building foundation ensures safety against soil shifting and provides a stable ground for your building to avoid the building collapsing during or after construction.
In this article, we will dive into the four types of building foundations for your building and the right foundation that supports your structure, whether it’s a residential building or a commercial building.
DEFINITION FOR FOUNDATION
The foundation serves as the lowest part of the building structure, providing a firm footing to transfer load, ensure stability, protect against moisture, and prevent settlement. The components that make up the foundation include the foundation footing, foundation wall, reinforcement, and oversight concrete.
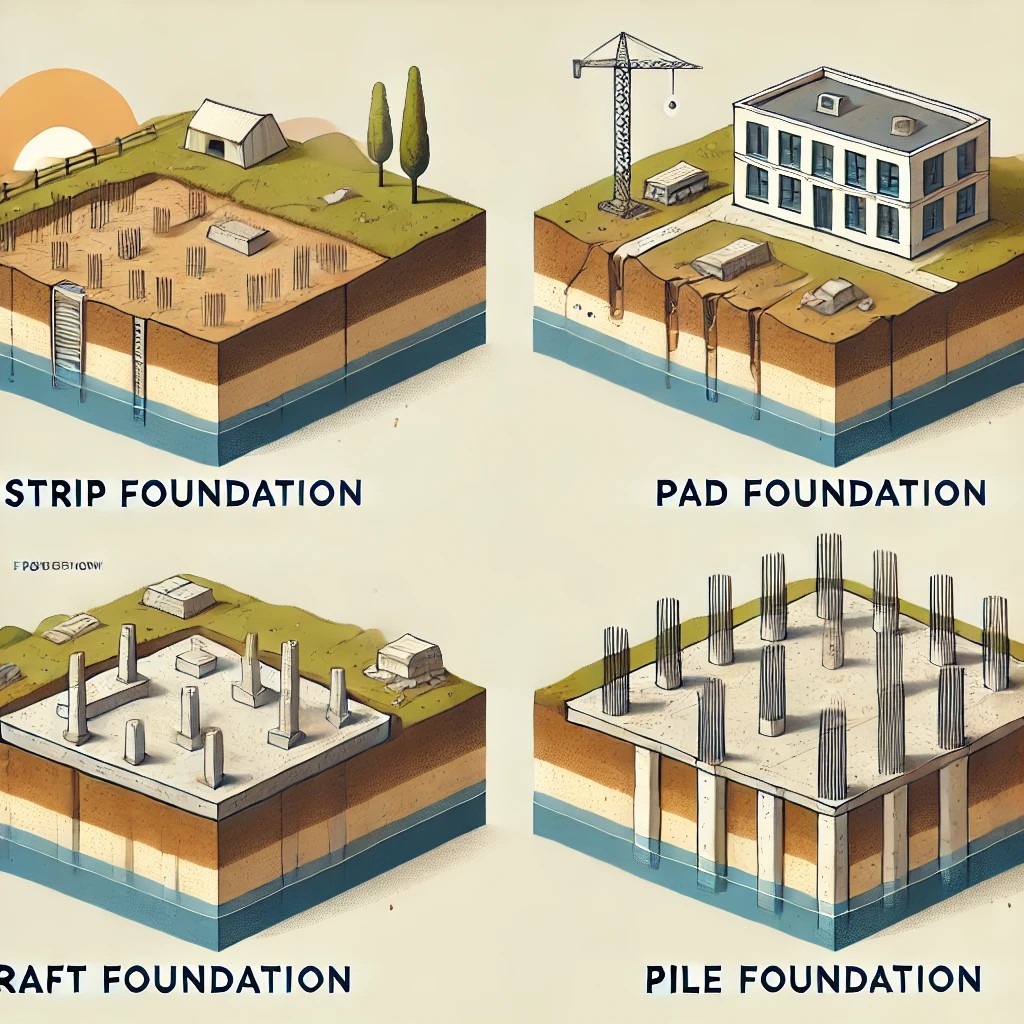
FOUR TYPES OF BUILDING FOUNDATIONS
The four types of building foundations that will be discussed include: strip foundation, pad foundation, raft foundation, and pile foundation.
Strip Foundation
A Strip foundation is a shallow foundation used within a low-medium-rise residential building, small commercial building, and area with firm and load-bearing soil. It’s suitable only where the subsoil is of good bearing capacity. This foundation spreads the building weight across a large area, which makes it a good choice for lightweight structures. Strip foundations are commonly used in Nigeria because of their simplicity, cost, and good for local soil conditions.
The various types of strip foundations are: wide strip, deep strip, and plain concrete strip foundation.
Pad foundation
Pad foundations are shallow foundations that transfer load from columns or structural elements to the soil. These foundations act as individual footings, supporting isolated columns with concrete slabs or pads beneath each load-bearing point. This type of foundation ensures efficient load transfer and structural stability. A Pad foundation is good for buildings with multiple columns, industrial structures, and sites with relatively good soil.
Raft foundation
Builders use raft foundations, or mat foundations, in areas with weak soil, like muddy or sandy soil. Raft foundations reduce pressure on a single-point load, preventing sinking or uneven settlement. This foundation suits high-rise buildings and large structures with substantial loads, uneven ground, and high groundwater levels. Raft foundations are ideal for large structures in areas with low soil-bearing capacity and differential settlement risks.
pile foundation
A pile foundation is a deep foundation with a greater depth than width. It transfers the building load to a more stable soil layer or bedrock, deeper than a shallow foundation. Concrete, steel, or timber piles drill deep into the ground to support structures that shallow soil cannot sustain due to poor quality or heavy loads.
COMBINED FOUNDATION AND REASONS FOR COMBINING FOUNDATION.
Builders use strip and pad foundations as combined foundations to distribute loads and adequately support the foundation, preventing the risk of differential settlement. Uneven soil areas may require a combined foundation to give excellent support to the building. A warehouse with a heavy load due to the vibration of the machine allows for a combination of foundations. The main reasons for combining foundations are: adjusting to the varied load types; material optimization and cost efficiency; enhanced structural integrity for complex designs; and so on.
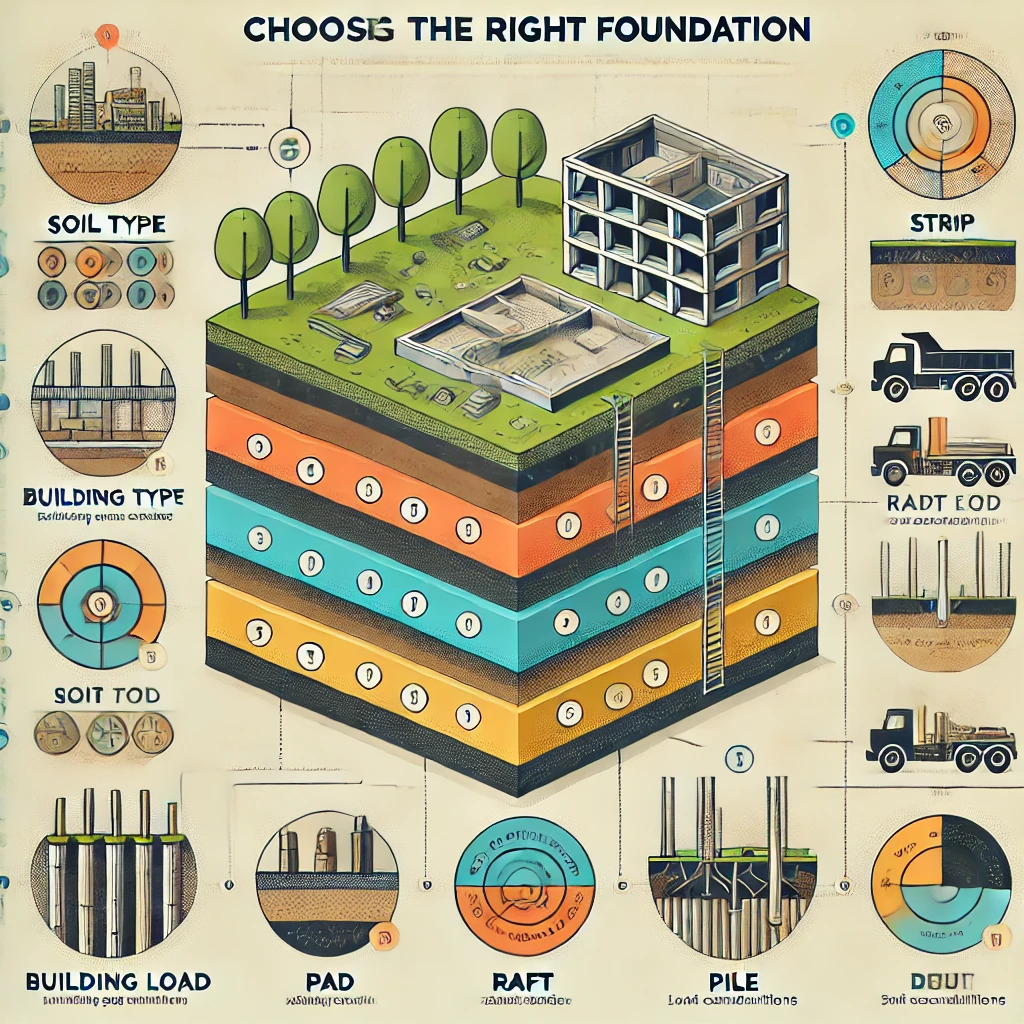
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT FOUNDATION FOR YOUR BUILDING.
The right foundation supports not just the building weight but also the soil and site condition. Here are some tips on how to choose the right foundation for your building.
Combined foundations using both strip and pad foundations are an effective solution in construction, particularly when dealing with diverse loads and soil conditions. This approach maximises load distribution, improves stability, and enhances cost efficiency while ensuring the structural integrity of the building.
However, combining pad and strip foundations offers a cost-effective and good solution for structures found with different soil conditions. By balancing the economy with structural integrity, combining pad and strip foundations provides a flexible solution for many modern construction projects.
Analysis of site conditions.
It’s very important to analyse if your site is on a gently sloped area or uneven ground, and buildings on a sloped site need special foundation design. Climate and environmental conditions like wind and rain exposure to extreme weather may require reinforced foundations.
Consider the building load.
The different loads on the building spread to the foundation include the dead load, live load, and wind load. Dead loads are the permanent weights on the structures that, when removed, can create a hazard effect on the structure like the walls, roofs, floors, etc. Objects that can be moved in or out of the structure, such as occupants, furniture, and temporary loads, contribute to live loads without causing any damage to the building, while external forces from the wind account for wind loads.
Consulting a structural engineer
A qualified structural engineer can recommend the best foundation for your building by working hand in hand with the geotechnical engineer to interpret the soil test and evaluate building regulations and requirements for your construction. They also calculate the total weight of the building to determine how it will be distributed across the foundation. In summary, the structural engineer guides you through analysing soil, load assessment, and site evaluation to pick the foundation that best suits your project.
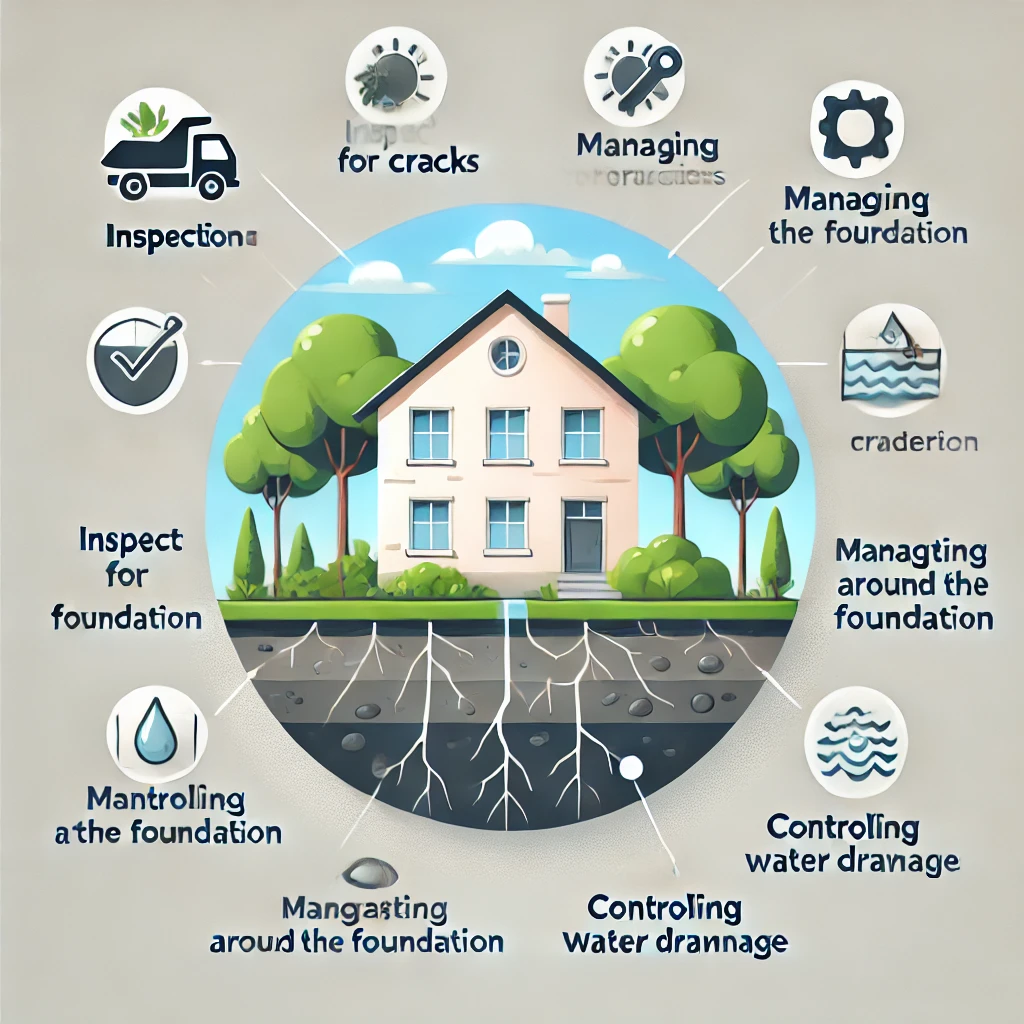
FOUNDATION MAINTENANCE TIPS
Inspect for cracks.
Widening cracks can indicate structural problems, and when this happens, it’s advisable to notify the structural engineer so as to rectify the problem on time. Also, examine the load distribution to ensure there is an even distribution of weight on the foundation. Uneven distribution can lead to stress on the foundation beam and extra cracking.
Managing vegetation around the foundation.
Proper maintenance of trees, shrubs, and other plants can help prevent soil shifting issues. It’s necessary to take note that overwatering plants near the site need to be avoided. Planting trees and shrubs at a good or safe distance from the foundation is very crucial, as it protects the foundation from damage and ensures long-term stability.
Control water drainage around your foundation.
Not providing proper drainage around your foundation might cause water collection. To avoid damage and erosion, it’s necessary to control water drainage around your foundation. Therefore, maintaining gutters and monitoring water flow can help safeguard the foundation.
CONCLUSION
Each foundation type offers unique advantages and characteristics. Understanding the Types of Building Foundations is crucial for selecting the right foundation for your building. Consulting a structural engineer ensures the foundation meets safety and regulation standards, providing the strength needed to support structures against time and environmental challenges.